Centrifugal Compressors
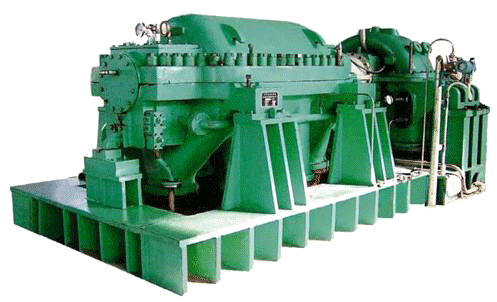
Centrifugal compressors use a rotating disk or impeller in a shaped housing to force the gas to the rim of the impeller, increasing the velocity of the gas. A diffuser (divergent duct) section converts the velocity energy to pressure energy. They are primarily used for continuous, stationary service in industries such as oil refineries, chemical and petrochemical plants and natural gas processing plants. Their application can be from 100 horsepower (75 kW) to thousands of horsepower. With multiple staging, they can achieve extremely high output pressures greater than 10,000 psi (69 MPa).
Many large snowmaking operations (like ski resorts) use this type of compressor. They are also used in internal combustion engines as superchargers and turbochargers. Centrifugal compressors are used in small gas turbine engines or as the final compression stage of medium sized gas turbines. Sometimes the capacity of the compressors is written in NM3/hr. Here 'N' stands for normal temperature pressure (20°C and 1 atm ) for example 5500 NM3/hr.